Lithium-sulfur battery solid-state battery manufacturing process flow
Lithium-sulfur batteries and solid-state batteries are two different battery technologies, and their manufacturing processes are also different. The manufacturing processes of lithium-sulfur batteries and solid-state batteries are introduced below.
Lithium-sulfur battery manufacturing process flow:
- Preparation of positive electrode materials: First, prepare positive electrode materials such as lithium sulfide (Li2S) or lithium sulfide composite. Usually chemical synthesis or thermal decomposition methods are used;
- Preparation of negative electrode materials: Prepare negative electrode materials such as graphite and silicon. Graphite can be prepared by chemical vapor deposition (CVD) or liquid phase exfoliation, and silicon can be prepared by thermal oxidation or ball milling;
- Electrolyte preparation: Prepare organic solvents containing lithium salts, such as carbonate solvents of lithium hexafluorophosphate (LiPF6).
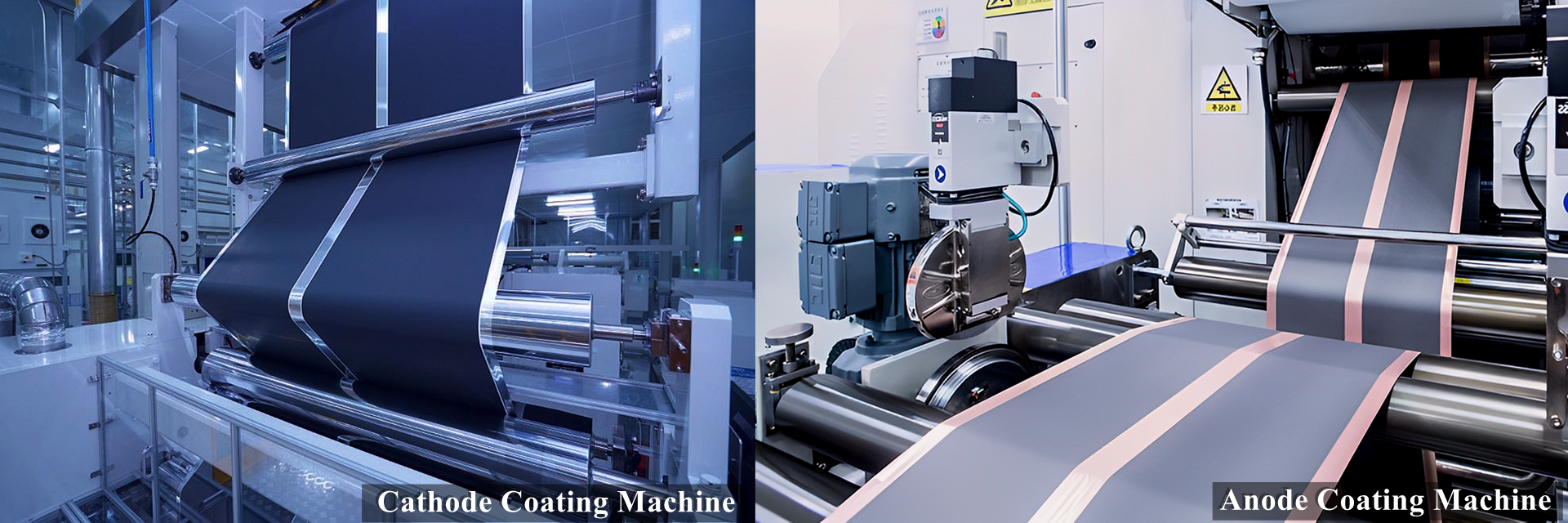
- Electrode coating: Coat the positive electrode material and negative electrode material on current collectors such as aluminum foil and copper foil respectively. Coating methods include solution coating, spray coating, roller coating, etc;
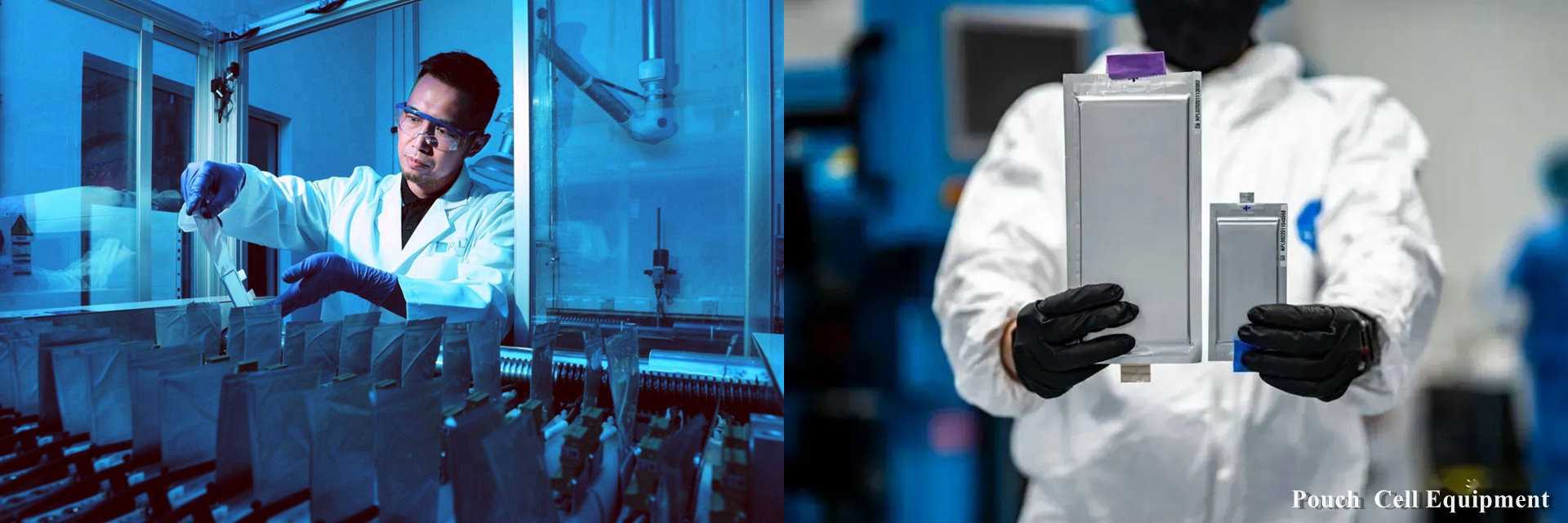
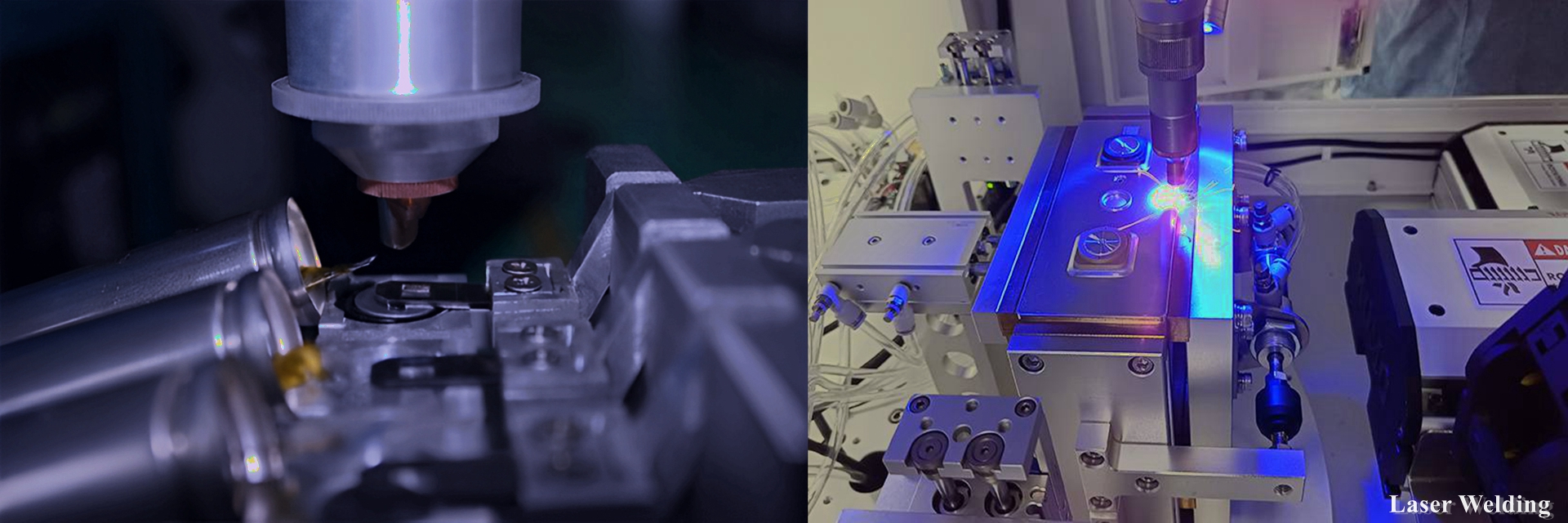
- Assemble the battery: Assemble the current collector, separator (porous polymer or cellophane) and electrolyte coated with positive and negative electrode materials into a battery. Pay attention to keeping the battery components clean and dry during assembly;
- Battery packaging: The assembled battery is packaged, usually with aluminum plastic film, aluminum shell or steel shell. During the packaging process, attention should be paid to the safety performance of the battery, such as preventing short circuit and overcharging;
- Formation and charge and discharge testing: Perform formation treatment on the packaged battery to make the battery reach the working voltage. Then conduct a charge and discharge test to check whether the battery performance meets the requirements;
Solid-state battery manufacturing process flow:
- Solid electrolyte preparation: Prepare solid electrolyte materials, such as lithium oxide (Li20), lithium sulfide (Li2S) or polymer electrolyte, etc. Preparation methods include solid phase reaction, molten electrolyte casting, etc;
- Electrode material preparation: Prepare electrode materials such as lithium metal, lithium alloy or transition metal oxide. Preparation methods include physical or chemical deposition, sputtering, etc;
- Electrode coating: Coat the electrode material on the current collector. Coating methods include solution coating, coating, roller coating, etc;
- Assemble the battery: Assemble the current collector, solid electrolyte and electrode interface material coated with the electrode material into a battery. Pay attention to keeping the battery components clean and dry during assembly;
- Battery packaging: The assembled battery is packaged, usually with aluminum plastic film, aluminum shell or steel shell. During the packaging process, attention should be paid to the safety performance of the battery, such as preventing short circuit and overcharging;
- Formation and charge and discharge testing: Perform formation treatment on the packaged battery to make the battery reach the working voltage. Then conduct a charge and discharge test to check whether the battery performance meets the requirements;
It should be noted that the above process flow is only the basic steps for manufacturing lithium-sulfur batteries and solid-state batteries. The specific manufacturing process flow may be adjusted according to the design and requirements of different batteries. In addition, as battery technology continues to develop, new manufacturing processes and materials are constantly emerging.